
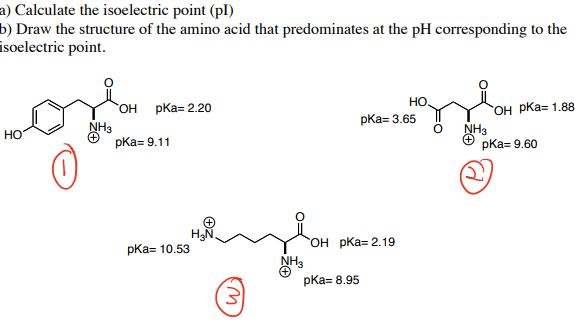
How does all this relate to the Isoelectric Point or pI? Tutorial: Amino Acid Charge – Zwitterions and Isoelectric PointĪmino Acid Stereochemistry R/S, D/L, Fischer ProjectionsĪmino Acids are biologically active molecules. Zwitterions:Įver notice that amino acids are written with both a positive N and negative O in the same structure? Why? How do you determine the charge of any group within an amino acid or polypeptide? This video walks you through the polar neutral, acidic, and basic amino acids and their side chain characteristics. Hydrophilic amino acids are rather ‘exciting' and reactive compared to the hydrophobic groups. This video explains their names, and side chain functional groups/structure. Hydrophobic amino acids feature water fearing neutral and non-polar side chains. These amino acids may appear out of place in an aqueous biological environment, but they are in fact critical to completing the amino acid picture. Hydrophobic Non-Polar Neutral Amino Acids This tutorial breaks down the side chain groups to help you understand their individual classifications. You need to UNDERSTAND how each specific R-group contributes to that groups chemistry and participation in 3-dimension structures and reactions. It's not enough to memorize names and structures.
Tutorial: Understanding Amino Acid Side-Chain Characteristics This video will help you set the stage for the entire series. What is so special about this biomolecule? What is the logic behind ‘alpha carbonyl' and why are there polar and non-polar, acidic and basic side chains.
Calculate pi isoelectric point series#
This tutorial series will walk you through the different aspects of amino acids as required for the MCAT. Amino Acids are the building blocks of living things playing key roles in cellular structure, function, and so much more. Therefore I modeled the 3D structure of the protein and I tried several other visualization programs to calculate this pI value, but I was not successful.Amino acids are critical for the MCAT as well as your biology and biochemistry courses. > I know the average isoelectric point of the whole protein, but there would be much more informative, to know what is the average isoelectric point of the proteins solvation shell, I think. > I am struggling with the overexpression and purification of a cytoplasmic protein that looks to be soluble only in a very narrow pH range. > On Nov 20, 2015, at 5:37 AM, Csaba Nagy wrote:

UCSF Computer Graphics Lab (Chimera team) and Babbitt Lab If the solvation shell is only water they will all be considered to have formal charge of zero, so the system will have the same net charge as the protein alone.

The net charge would be reported in the Reply Log (open from Favorites menu). It will ask you to add hydrogens first if you don’t already have them. You could only get the net charge of the system after using Add Charge (in menu under Tools… Structure Editing). Sorry no, there is no such calculation in Chimera.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
